Support
Google Tag Manager Tracking
This article shows you how to implement Google Tag Manager inside of your site. To learn how to create GA4 tags in Google Tag Manager, see Google's documentation.
Note
Google Analytics 4 is replacing Universal Analytics. On July 1, 2023 all standard Universal Analytics properties will stop processing new hits. 360 Universal Analytics properties will stop processing new hits on July 1, 2024. To learn how to migrate, see Make the switch to Google Analytics 4.
How to Add Google Tag Manager
To add Google Analytics to your site:
- In the left panel, click SEO & Settings, and then click the Google Tools tab.
- Type your Google Tag Manager ID.
- Type Enter to confirm.
Invalid Google Tag Manager ID
This means your Google Tag Manager ID is invalid or misspelled.
Set Up Google Tag Manager
Warning
This step is critical in allowing Google Tag Manager tracking inside your site.
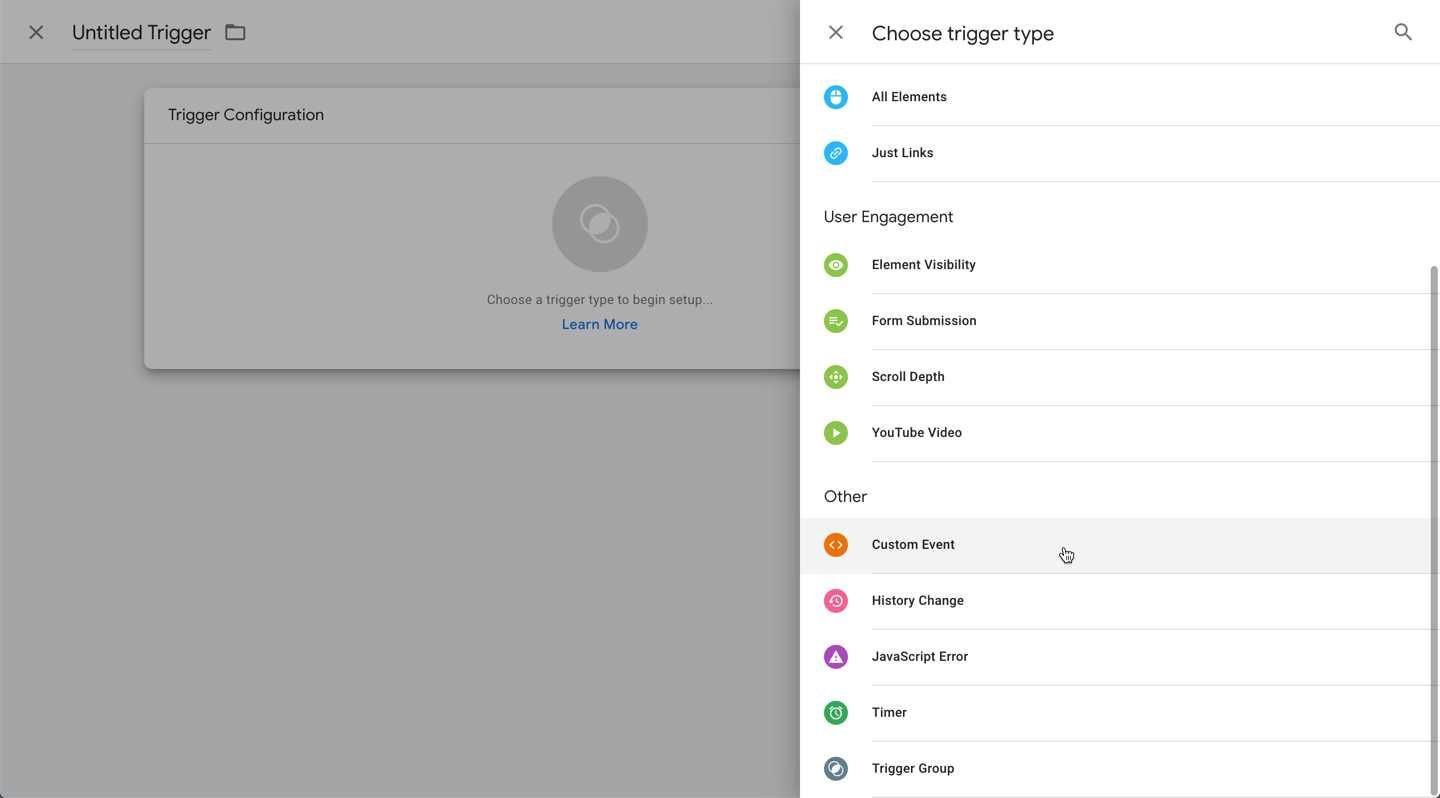
Next, we need to replace the default All Pages page view trigger with our custom event. Inside of tag manager, we need to first create the custom event trigger:
- Go to Google Tag Manager and sign in.
- On the left, click Triggers.
- On the right side, click the new button.
- Type a name for the trigger at the top left. We recommend something memorable and helpful, such as: Custom Page View Trigger.
- Click the custom trigger configuration box and select Custom Event.
6. Google Tag Manager Tracking
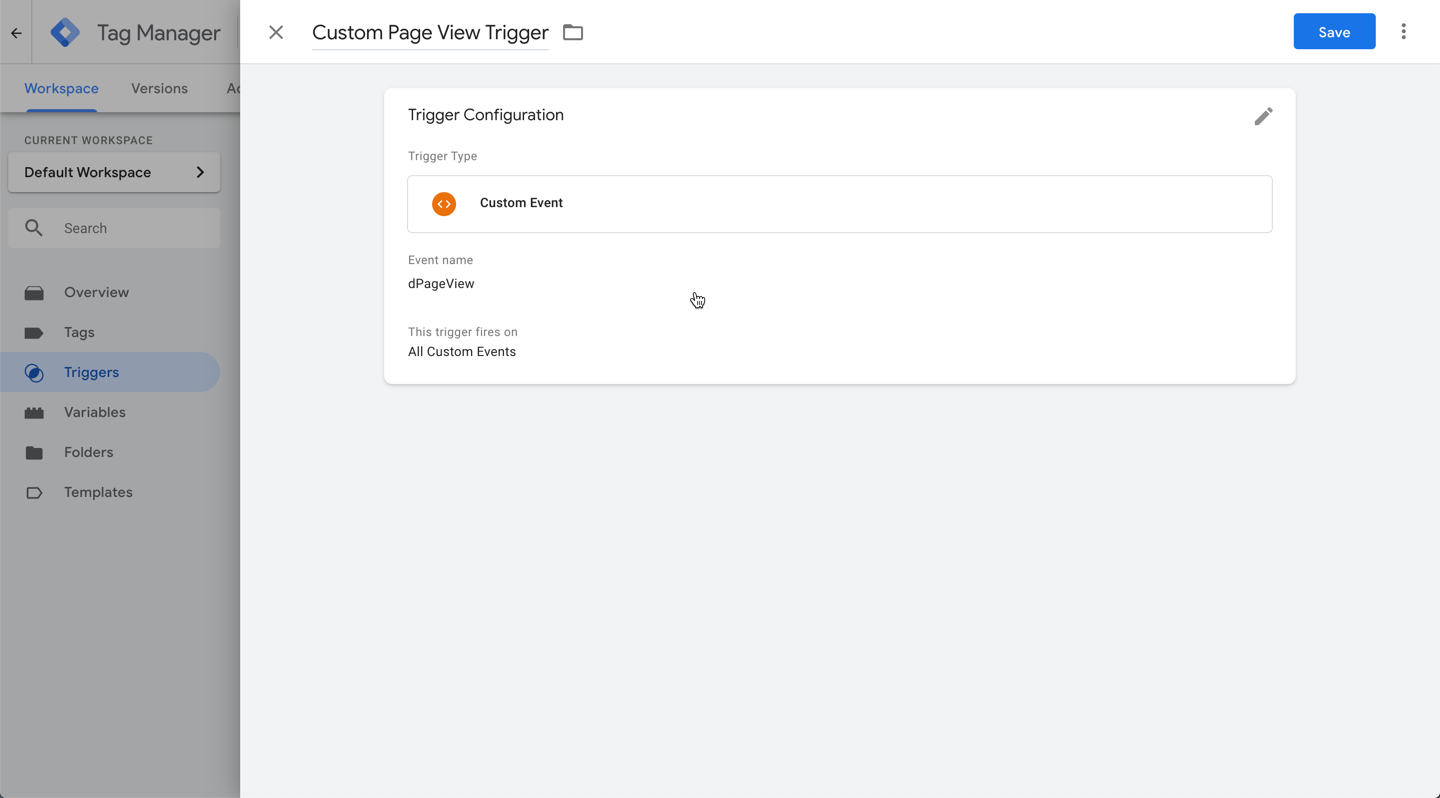
7. Click save in Tag Manager.
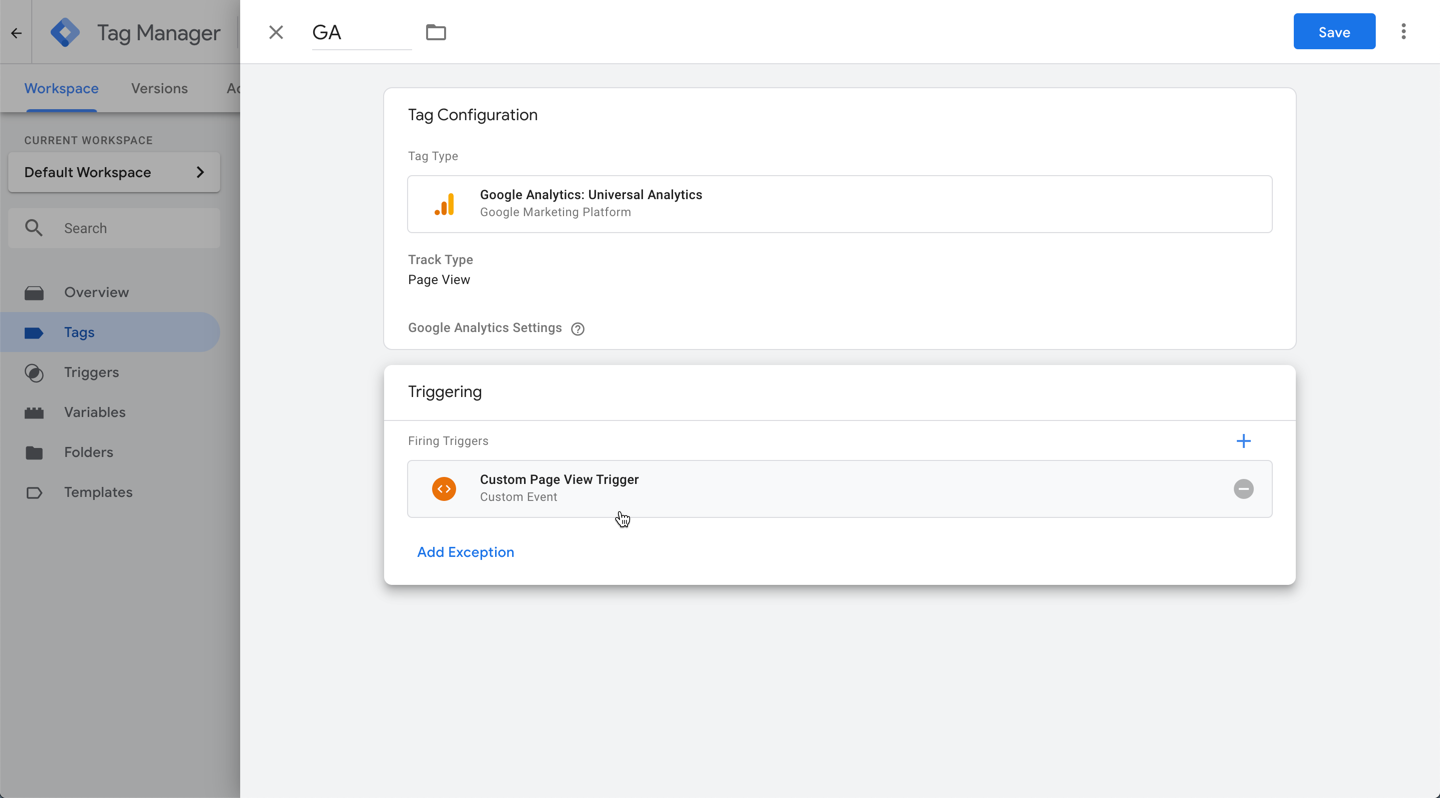
After creating the trigger, we need to apply it to the tags we want. This needs to be done for every tag you use on the site to trigger for page view events. In this example, we apply it for Google Analytics Universal, however Google Analytics 4 is the newest version we recommend you use. To learn how to create and apply triggers to GA4 tags in Google Tag Manager, see Google's documentation.
- In Tag Manager, go to tags.
- Create a new tag.
- Type a memorable name.
- Click the Tag Configuration box and select the tag you want to use. In this case, Google Analytics Universal.
- After setting up the tag, click the Triggering box. Choose the custom trigger we created Custom Page View Trigger.
Note
6.If there’s already the All Pages trigger applied, please delete it. We only need the custom trigger to run.
7.Select a new variable.
8.Select Google Analytics Settings.
9.Type your GA tracking ID, and type a name for your variable at the top. Select the variable and click Save.
After you have made these changes to Tag Manager, click Submit and then Publish the changes to the live settings.
Considerations for Google Tag Manager
- This code will only run on the live published site. You will want to make sure you test it on the live version.
- We have completed extensive testing and the
body-end.htmlsection of Developer Mode works for adding the noscript code and default code. - Please do not change the ‘dataLayer’ setting from Google Tag Manager, this will break our custom integration code.







